[ The PC Guide | Systems and Components Reference Guide | Hard Disk Drives | Hard Disk Interfaces and Configuration | Integrated Drive Electronics / AT Attachment (IDE/ATA) Interface | IDE/ATA Configuration and Cabling ]
Windows Drivers and DMA Support
Traditionally, support for IDE/ATA hard disks has been provided by the system BIOS and operating system. This support was at first limited the simple programmed I/O (PIO) access modes. Over time, the IDE/ATA world has moved away from PIO towards DMA modes. At first this was because DMA modes allow hard disk transfers to occur without excessive CPU utilization--PIO modes drag down the CPU while DMA modes allow transfers to occur while letting the CPU do other things. With the introduction of Ultra DMA, DMA support became that much more important.
DMA began to rise in popularity at around the time the first version of Windows 95 was released. Unfortunately, Windows 95 "A" did not have native support for first-party bus mastering DMA, so special drivers had to be added to support DMA. These frequently caused compatibility and stability issues, and it took several years for DMA support to "mature". Starting with the second OEM-only release of Windows 95 ("OEM SR2", "Windows 95b") DMA support was provided by the operating system. Windows 98 and Windows ME also provide built-in support for DMA operation, and DMA works quite well today.
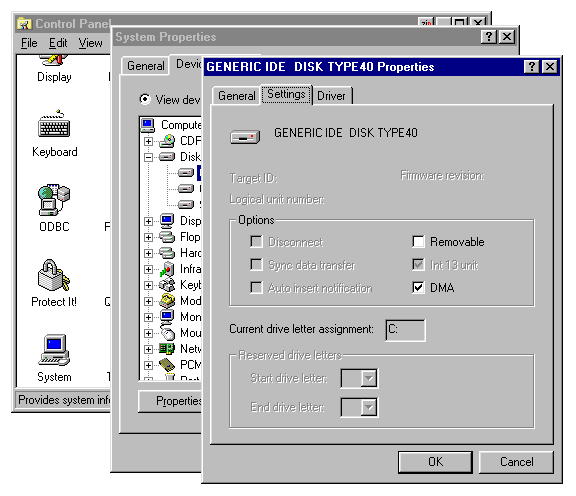
On modern systems, DMA support should be enabled by default. You can check for DMA support by looking in the Device Manager. From the Control Panel, open "System", then click the "Device Manager" tab. Open the icon for "Disk drives", and then highlight the drive you are interested in. Click "Properties" and then the "Settings" tab. Among the other settings you should find a "DMA" check box, which should be checked. If it is not, try checking it to enable DMA support. If you then reboot and the check box does not stay checked, this probably means your system does not support Ultra DMA; try looking on this page to be sure you meet all the requirements.
|
The "Settings" page for a DMA-capable hard
disk under Windows 95, |
![]() Note: Hard drives
connected to some Ultra DMA add-in controllers will not display a "DMA
checkbox". Since these cards are designed primarily to provide Ultra DMA
support, they don't bother showing it as an explicit option.
Note: Hard drives
connected to some Ultra DMA add-in controllers will not display a "DMA
checkbox". Since these cards are designed primarily to provide Ultra DMA
support, they don't bother showing it as an explicit option.
![]() Next: Performance Factors and Tradeoffs in Configuring
for Multiple Devices
Next: Performance Factors and Tradeoffs in Configuring
for Multiple Devices
| The PC Guide
(http://www.PCGuide.com) Site Version: 2.2.0 - Version Date: April 17, 2001 © Copyright 1997-2004 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved. |
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site. Please read the Site Guide before using this material. |